AC Recharge
As the Air Conditioning System ages and parts become worn, it becomes necessary to replace the refrigerant in the system. This is especially true if a component is replaced and the system is opened, as all refrigerant will escape and the A/C system will immediately become non-functional.
Converting your system to R134A before recharging? Check out: R134A Conversion.
Contents
Precautions
The following precautions should be observed when servicing the A/C system.
- Do not release refrigerant into the air. Use only approved recovery/recycling equipment to capture the refrigerant every time an air conditioning system is discharged.
- Always wear hand and eye protection.
- Do not store refrigerant in containers above 120 degrees F.
- Do not heat refrigerant container with an open flame. If warming the refrigerant can is required, place the bottom of the container in warm water.
- Do not drop or puncture refrigerant containers as they are under high pressure.
- Refrigerant will displace oxygen--be sure to work in a well-ventilated environment to prevent suffocation.
- Do not introduce compressed air to any refrigerant container or refrigerant component.
- When compressor is removed, store in the same orientation as it would be mounted on the engine.
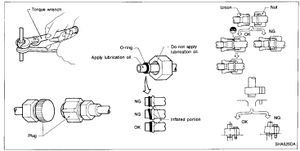
- When tightening union joints, always use a back-up wrench.
- When installing air conditioning components, connect the tubes as the final stage. Don't remove the caps until a component is ready for installation.
- When connecting a tube, always use lubricant on the o-rings.
- O-ring should be attached near the "inflated" (barbed) portion of a tube.
Tools Needed
- A/C Vacuum Pump
- A/C Vacuum Manifold Gauges
- Approx 36oz of refrigerant (R12 [90-93] or R134A [94+])
- Approx 4oz of compressor oil (Ester oil for R12 systems, PAG oil for R134A systems).
Parts Needed
- If the system has been open and exposed to the atmosphere, it is recommended you replace the receiver/drier.
- When replacing/removing ANY A/C component, always install new o-rings, following the guidelines shown above.
Procedure
Evacuating
Note: If removing old refrigerant, be sure to remove it properly and not just vent it to the atmosphere.
It is essential to completely remove air and moisture from inside the refrigeration system before charging. This process is called evacuation. If the air conditioning system is operated without complete evacuation, the following abnormalities may result.
- Poor cooling due to reduction in the thermal exchange rate in the condenser.
- Moisture recirculating together with refrigerant through the refrigeration system freezes at the port of the cold expansion valve. This impedes the normal refrigerant flow, thus lowering the cooling efficiency.
- The refrigerant reacts with water chemically, generating corrosive hydrochloric acid thus causing corrosion to the refrigeration system components.
Evacuating must be done with manifold gauges. For complete instructions, see the Manifold Gauges article.
Charging
- If you're not using the manifold gauge hoses to charge the system, close their service valves and remove them from the car now.
- Connect refrigerant can to the low pressure port on the car.
- If you are using the manifold gauges (not a bad idea), close the high pressure valve and vacuum service valve (if not already done), and open the low pressure valve to allow refrigerant to enter the system.
- After connecting the refrigerant to manifold gauges, open the top of the charging (yellow/green) hose just slightly for about two seconds. This helps fill the hose with refrigerant, so you avoid any air entering the system.
- Start engine and set climate control to maximum cooling (AUTO/60 degrees for auto climate control; slider at blue, fan speed 4 and A/C switch on for manual climate control).
- Charge approximately half a can (7.05oz).
- You should hear the compressor click on shortly while adding refrigerant. If not, there's a fault in the wiring preventing the compressor from engaging.
- Once the compressor turns on, continue to charge the refrigerant. As the refrigerant level in the can becomes low, it helps to gently agitate the can to increase the pressure in the can. Avoid turning it over or shaking it violently. It just needs a little bit of agitation.
- It also helps to put the refrigerant can in a pot of hot (not boiling) water, as it will increase the pressure in the can and help the refrigerant enter the car's A/C system quicker.
- When the can feels empty, close the port and switch to another can. It can sometimes take quite a while (say, 10 minutes) to fully empty a can of refrigerant.
- Complete the charge, ensuring the pressures reach their ideal range as seen in the chart below. Ambient temperature will affect the ideal ranges. If you've replaced major A/C components (condenser, compressor, etc) add a small amount of oil. Refer to the Compressor Oil section of the Air Conditioning System article for more info.
- Close all lines, shut off the car, and carefully remove any gauges/hoses still attached.
- There will be quite a lot of pressure trapped in the manifold gauge lines, be cautious.
- Enjoy your A/C!
Ideal Pressures
Ideal pressure ranges are slightly different depending on the type of refrigerant used.
R12
| Ambient Air Temperature |
Low-pressure Side |
High-pressure Side |
|---|---|---|
| 68°F |
10.0 - 14.9 psi |
114 - 139 psi |
| 77°F |
17.2 - 21.8 psi |
132 - 161 psi |
| 86°F |
24.3 - 29.7 psi |
164 - 201 psi |
| 95°F |
31 - 37.8 psi |
196 - 240 psi |
| 104°F |
37.5 - 45.5 psi |
229 - 279 psi |
| 114°F |
44.1 - 54 psi |
260 - 320 psi |
R134A
| Ambient Air Temperature |
Low-pressure Side |
High-pressure Side |
|---|---|---|
| 68°F |
26.3 - 32.1 psi |
149 - 181 psi |
| 77°F |
26.9 - 32.8 psi |
162 - 199 psi |
| 86°F |
32.0 - 39.1 psi |
195 - 237psi |
| 95°F |
39.1 - 47.6 psi |
228 - 279psi |
| 104°F |
46 - 55 psi |
263 - 320psi |
Off-the-shelf recharging kits will only give you the low-pressure reading, but this should be enough (under most circumstances) to properly charge the system. Under no circumstances should you add refrigerant past the recommended capacities/pressures, as it can and will cause serious damage to your A/C system.
Manifold Diagnostics
Using Manifold Gauges, you can quickly and easily diagnose performance problems with your A/C system. Refer to the parent article for more information on doing this.